Software Engineering and Management Education
A challenge in software engineering education is to give students sufficient hands-on experience in actually building software. This is necessary so that students can understand which practices and techniques are useful in various situations. In this context, serious games are increasingly considered a powerful instructional method and various games are being developed.

Gresse von Wangenheim, C.; von Wangenheim, A. Ensinando Computação com Jogos.
Editora Bookess, 2012 (in portuguese).
Teaching Software Project Management with Games – TV report (in portuguese)
Gresse von Wangenheim, C. Como Ensinar com Jogos?
CQ – XIII Curso de Qualidade no XXXII Congresso da Sociedade Brasileira de Computação, Curitiba, 2012. slides (in portuguese) or assist a reproduction of the talk on youtube (in portuguese)
Gresse von Wangenheim, C; Shull, F. To Game or not to Game?. IEEE Software, 26(2), 2009. (extra material)
PETRI, G.; GRESSE VON WANGENHEIM, C.; BORGATTO, A. F. Quality of Games for Teaching Software Engineering: An Analysis of Empirical Evidences of Digital and Non-digital Games. IEEE/ACM 39th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering Education and Training Track (ICSE-SEET), Buenos Aires/Argentina, 2017.
Petri, G., Gresse von Wangenheim, C., Borgatto, A. F., Calderón, A., & Ruiz, M. Digital Games for Computing Education: What Are the Benefits?. In A. Krassmann, É. Amaral, F. Nunes, G. Voss, & M. Zunguze (Eds.), Handbook of Research on Immersive Digital Games in Educational Environments (pp. 35-62). Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2018.
BATTISTELLA, P.; GRESSE VON WANGENHEIM, C. Games for Teaching Computing in Higher Education – A Systematic Review. IEEE Technology and Engineering Education (ITEE) Journal, 9(1), 8-30, 2016. (draft)
Project management (PM) is the discipline of planning, executing, monitoring and controlling resources to successfully complete a project. It is a key factor for delivering successful projects on time and within budget. In recent years, all business sectors, including the software sector, have increasingly recognized PM as a core competence. As a consequence, the need for project managers has never been greater than today and the need for PM education and training in the software sector grows.
In this context, serious games have become an alternative offering various advantages. They can help to reinforce basic concepts. Games can also contribute to teach higher-cognitive competencies illustrating their application and relevance with acceptable training time and instructor load. And, building on the engaging nature of games, they can make learning more fun, if not easier.
Examples of Educational PM Games
- PM Master
- Detective Game – what killed the project?
- Earned Value Management Board Game
- Leadership exercise: Dealing with difficult people
- Applying SCRUM: Welcome to SCRUMIA
- SCRUM’ed – A 3D role-playing game to learn Scrum
- SCRUM-scape: A RPG to reinforce SCRUM concepts
- Kahoot PM Quiz
- Paper Tower Competition
Evaluation of Educational Games
Games are becoming increasingly popular for teaching. They are considered to result in a wide range of learning benefits like, increase of learning effectiveness, increased interest and motivation, and reduction of training time and instructor load. However, most of these claims seem not rigorously established due to a lack of sufficient empirical support.
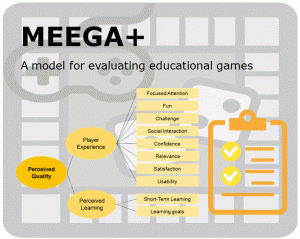
So in order to guide decisions about whether to use a games for certain educational purposes, we developed MEEGA+ a model for assessing the quality of educational games in terms of player experience and perceived learning from the viewpoint of the learners through case studies using a standardized questionnaire. Try it out here.
MEEGA+ has been developed in cooperation with GpTEc/UFSM.




